With rapid urbanization and population growth there is a significant increase in construction and demolition projects worldwide which generates a significant amount of waste. The annual construction waste is expected to reach 2.2 billion tons globally by 2025. Let us understand in detail what these waste are and whether they can be recycled.
Construction and demolition waste
Any waste that is generated from construction and demolition of buildings, roads, bridges, etc. constitutes construction and demolition (C&D) waste . It consists of materials that are mostly non-biodegradable and inert. 75% of the waste generated by the construction industry is not currently recycled /reused . Waste generated from the construction sector accounts for 30% of the total waste produced globally. The different types of C&D waste with examples are mentioned below:
Land clearing debris:

These include those materials or objects that are cleared out before the start of any construction or demolition activity in a site. Examples- Tree tops, tree stumps, rocks.
Demolition waste (from buildings):
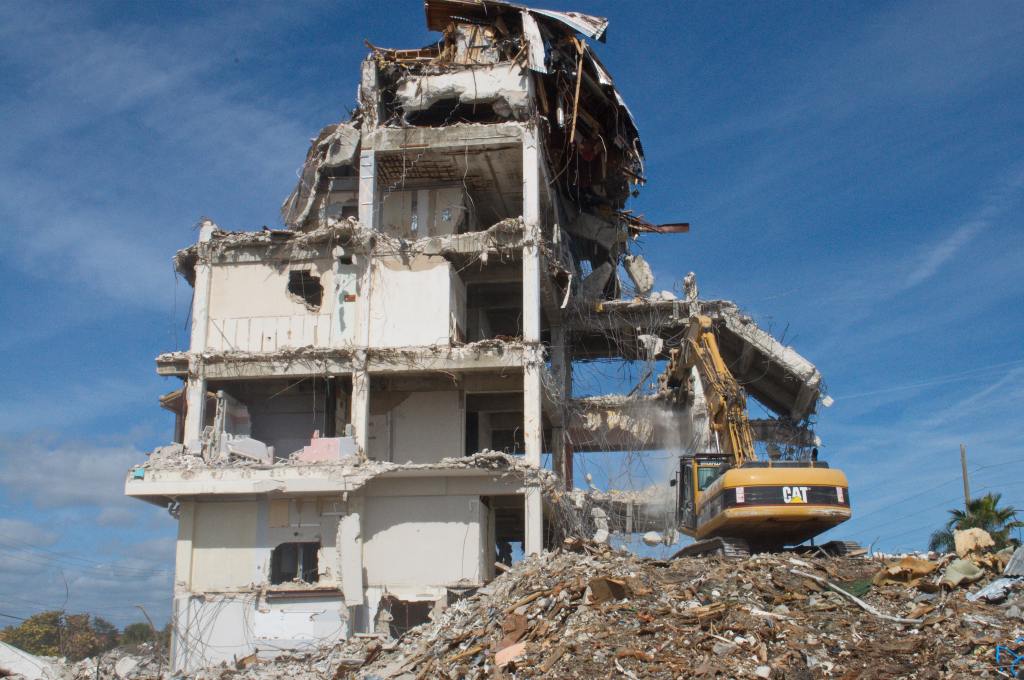

These include waste that are generated while demolishing a building. Examples: Concrete, wood, brick, plaster, roofing materials, plastic, glass, metals, insulation.
Concrete and bricks are used as foundation material. Plastics can be found in vinyl siding, doors, windows. Glass is used in windows, doors, glass shelves. Wood can be found in the form of plywood, chip wood, saw dust, etc.
Construction waste (from buildings):
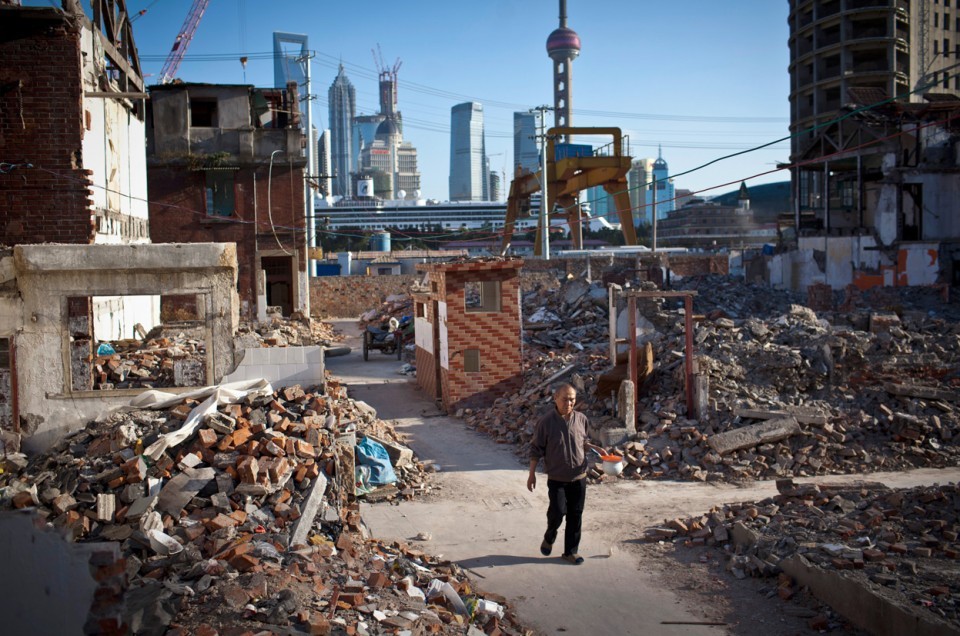

These include waste that are generated while constructing a building. Example: Leftover cement mix, insulation, asbestos, tiles, ceramics, metals, drywall, paints, varnishes, adhesives, sealants, bricks.
Asbestos is a mineral used to provide resistance to corrosion and heat and is used in several building materials like asphalt roofing, pipe insulation, ceiling and wall insulation, resilient floor tile, ceiling tiles, etc. Cement is generally used as a binding agent that sets, harden and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Drywall supports and sustains the walls, making them last longer. It is constructed using gypsum wallboard.
Highway construction and demolition waste:
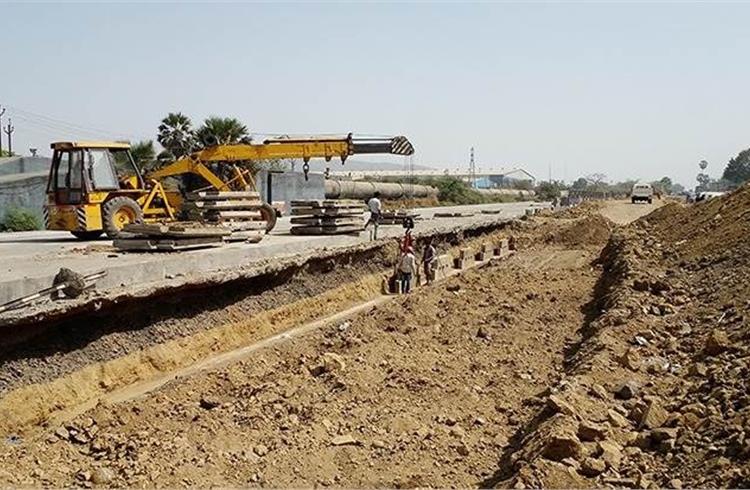

These include waste that are generated during construction and demolition of roads, bridges, flyovers, etc. Examples: Asphalt, fly ash, concrete, steel, brick, block, rock.
Asphalt is used as a binding agent for making roads and highways. Its smooth surface increase skid resistance.
Oversized municipal solid waste

These include discarded furniture, rugs, wall décor, bedding and other furnishing items.
Impact on the environment
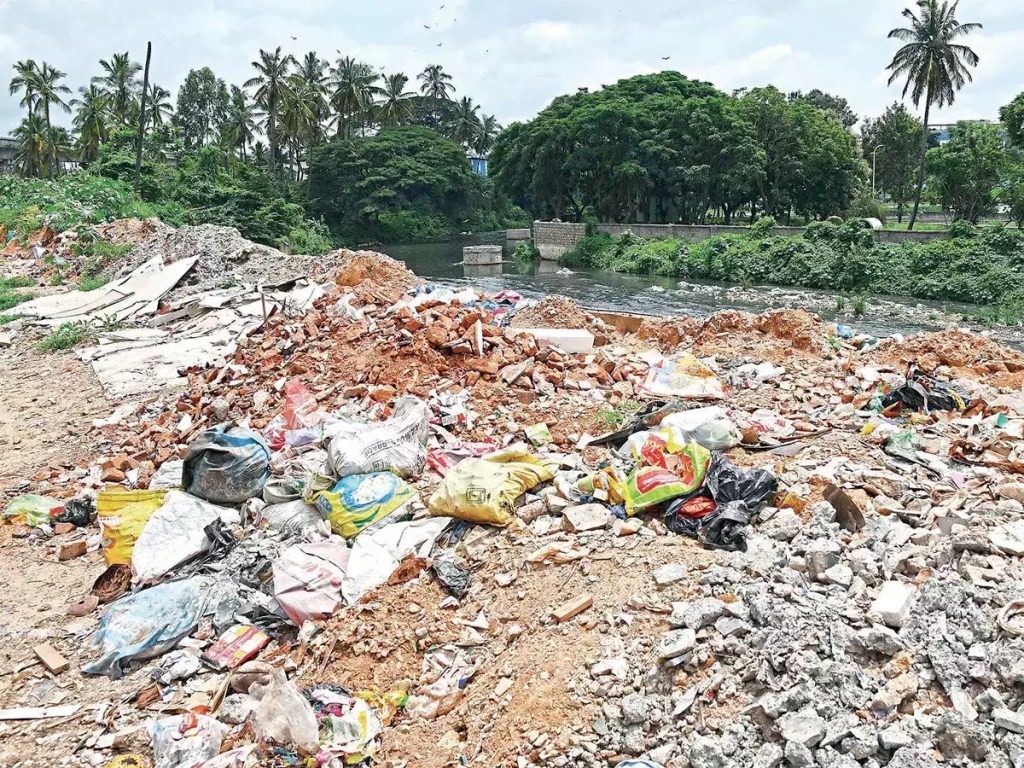

Although 90% of the C&D waste contain inert and non-hazardous materials that can be reused and recycled; like concrete, bricks, tiles, ceramics, metallic waste (copper, bronze, brass, etc.); remaining 10% contain hazardous materials that pose a threat to the environment, like asbestos, left-over paints, varnishes, adhesives, sealants, cement, aerosol cans, contaminated empty containers, etc. These harmful materials may reach the groundwater and surface water from landfills; where these waste are usually disposed; thereby contaminating them. From the surface water these materials may enter ponds and rivers, affecting aquatic life as well as animals consuming water directly from them. Sometimes C&D waste are dumped in water bodies which leads to various detrimental impacts on the environment. It interferes with the natural habitat of aquatic flora and fauna. It also results in increase in the level of water which could lead to floods. These huge piles of waste are also put together on roads, creating traffic congestion, or find its way into nearby municipal bins, making the waste heavy and degrades its quality for treatments like composting. It also enters into surface drains, thereby blocking them. C&D waste also carry dust, particulate matter, asbestos, etc., which may get mixed with air, thereby causing air pollution.
Proper use and re-use of construction materials will make the construction industry more economical and green and will thus aid in sustainable development.
How these waste can be managed?
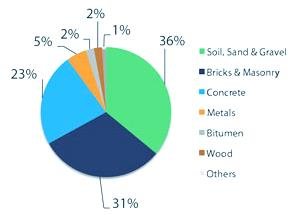
To manage C&D waste reduce, reuse and recycle policies should be applied. If we look at the Indian scenario, according to the Building Material Promotion Council (BMPTC), India generates almost 150 million tons of construction and demolition waste every year, but only 1% of it is recycled. The C&D waste is usually collected by the municipality along with other solid waste, thereby making it unsuitable for recycling. According to a study by the Technology Information, Forecasting and Assessment Council (TIFAC), 70% of the construction industry is not aware of the recycling techniques. 50% of the waste from C&D activities in India consists of concrete and masonry waste, still it is not being recycled. While it is being recycled in countries like U.K, U.S.A, France, Denmark, Germany and Japan. Table below shows the types of waste and whether they can be recycled/reused according to a study published in the International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts (IJCRT):
| C&D waste | Recycle/reuse potential | Biodegradable potential | Potential for landfilling |
| Concrete | Recycled aggregate for road base, and for concrete | No | Yes |
| Steel | Recyclable to steel | No | No |
| Brick and block | Backfill, recycled aggregate | No | Yes |
| Insulation | Insulate attic or as sound proofing on interior walls | No | No |
| Glass | Finer glass as pozzolans in cement | No | Yes |
| Ceramic | Possibly recyclable as filling material as a coarse aggregate for concrete | No | Yes |
| Aluminum | Recyclable to aluminum | No | No |
| Plastic | Recyclable to any form | Some can be biodegradable | Yes |
| Paint | Reusable as paint/concrete admixture | Some can be biodegradable | No |
| Wood | Recyclable to veneer board/paper pulp | Yes | Yes |
| Gypsum board | Recyclable to new board, crushed wall as clay and silt mixture and can be composed | Yes | No |
| Card board | Composting, fire kindling, paper production | Yes | Yes |
| Asbestos | No | No | If properly sealed |
For proper management of C&D waste environment friendly technologies are needed. Also using eco-friendly building materials will reduce the impact on environment. Generation of waste should be minimized as much as possible and recyclable materials should be sorted and segregated. In this way these materials can be saved from getting dumped in the landfill. Lets discuss the 3R’s (Reduce, reuse, recycle) of C& D waste in detail.
Reduce
The most important step in waste management is to generate less amount of waste. This can be achieved by proper use of resources, use of recovered materials, and also avoiding over-ordering of virgin material. In order to generate less waste standard quantities and size of materials should be considered. Also after demolition, usable items should be recovered to reduce waste generation.
Reuse
Reusing the intact materials from demolition sites in new construction projects is another way to manage waste. Left over or extra materials should be stored properly for future use. Salvaged materials can be used in current or future projects.
Recycling

The materials that can be used again and are valuable, can be prevented from being dumped into landfill by separating, collecting, processing and marketing. This process is known as recycling. These recycled materials can be used in new construction projects. To carry out recycling successfully the waste needs to be segregated properly according to their types and different types of waste should be stored in different containers.
The C&D waste management includes the following steps:
Storage and segregation
Storage of C&D waste should be done at the point of generation and scattering of the waste should be prevented. Materials should be stored in safe, secure and moisture free area.
Segregation can be done at the source i.e. during construction and demolition activities. It can also be done by removing the foreign materials from the mixed material by processing. In terms of energy utilization, economics and time, segregation at source is most efficient. It is necessary to segregate the waste into road work materials, structural building materials, salvaged building parts and site clearance waste.
Collection and transportation

When the C&D waste is stored in waste skips, skip lifters are fitted for efficient removal of waste. If it is stored in trailers, tractors are used to remove them. In case of very large volumes of waste, front-end loaders in combination with sturdy tipper trucks may be used to minimize the time taken for loading and unloading.
Recycling and reuse
Waste like concrete and masonry is recycled by crushing the debris into a granular product of given particle size. There are two types of recycling plants: Mobile and Stationary. For demolition waste, plants for processing of the waste is differentiated on the basis of mobility, type of crusher and process of separation.
Mobile recycling plant:
It consist of one crusher and some sorting devices. The removal of contaminants are mainly done by hand sorting and using self-cleaning electromagnets.
Stationary recycling plant:
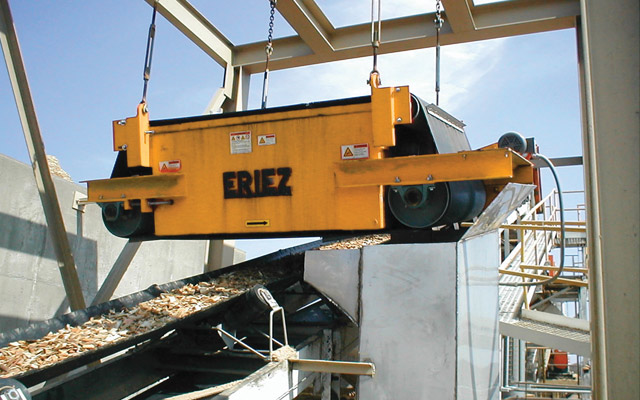

It usually consist of a large primary crusher working in conjunction with a secondary crusher and also includes various cleaning and sorting devices to produce high quality aggregates. In order to produce a clean recycled aggregate from a mixed and contaminated input material self-cleaning electromagnets, sieves and hand sorting are employed.
Disposal
As C&D waste are inert they do not react chemically with other materials. Hence they should be reused and recycled as much as possible. Special landfills are also there to dispose these inert materials. But recycling them will reduce the demand for more space for landfilling.
Oversized C&D waste like furniture can be recycled, especially those made of wood and metal. Damaged furniture can also be repaired in repair shops. Also one can donate or sell old furniture in charitable organizations. Upcycling is another way of handling old furniture.
Benefits of recycling C&D waste
Recycling and reuse of salvaged building materials reduces waste disposal costs and material expenses. It also reduces depletion of natural resources such as tress, oil and mineral. Through recycling there will be a reduction in manufacturing and transportation related emissions. Recycling of materials uses less energy and water, compared to the manufacturing processes using virgin material. Due to growing population less land is available for waste disposal. Recycling of materials from demolished concrete or masonry can be profitably used in different ways within the construction industry thus promoting circular economy.
Some of the startups working in the field of C&D waste management in India are- Sal tech design labs, Angirus, Recycle X, GreenJams, Hexpressions, Strawcture, etc.
Conclusion
As the demand for construction projects are increasing due to rapid urbanization and population growth, recycling and reuse of C&D waste is the need of the hour to make the construction industry eco-friendly and green. For this it is necessary to create awareness about the benefits of recycling among the people, contractors, architects, engineers, etc. More recycling plants should be installed and recycled aggregates should be used instead of natural ones. In this way one can protect the environment by using less virgin materials and also reduce the cost of disposing waste in landfills.


2 thoughts on “Can construction and demolition waste be recycled?”